In this articlal i will give a brief explanation of what generative AI is and has quickly become one of the most essential technological shifts of our time. From chatbots that hold surprisingly natural conversations to tools that generate artwork, music, and code in seconds, this technology is reshaping how we create, work, and interact with machines.
But beneath the hype, an important question remains: what exactly is generative AI, and why does it matter so much these days?
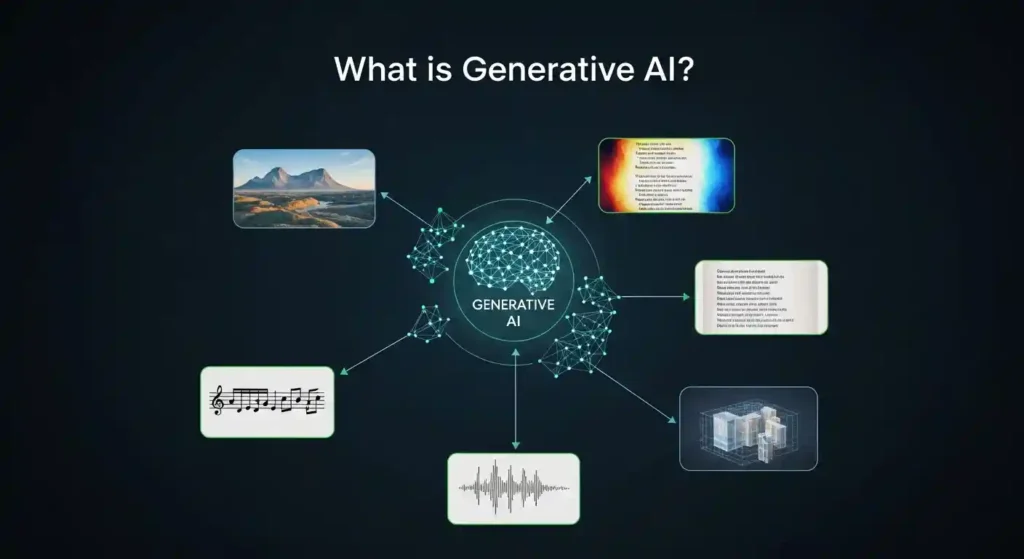
Understanding Generative AI
At its core, generative AI refers to artificial intelligence systems designed to create new content. This content can take many forms, such as text, images, audio, video, or software code. Unlike traditional AI systems, which focus on classification, prediction, or decision-making, generative AI produces outputs that did not previously exist.
To put it simply:
A traditional AI system might identify whether an image contains a cat or a dog. A generative AI system can create an entirely new image of a cat, one that has never existed before, based on what it has learned about how cats generally look.
The difference between traditional AI and generative AI is like the difference between a critic and an artist. One evaluates what already exists; the other creates something new.
How Does Generative AI Work?
Generative AI systems learn by analyzing massive amounts of data. During training, they study patterns, structures, and relationships within this data—learning the “rules” of language, images, sound, or code.
Modern generative AI models rely heavily on deep learning techniques. For text generation, architectures like transformers allow models to understand context and relationships between words across long passages. For images, diffusion models learn how to gradually transform random noise into coherent, realistic visuals.
A helpful analogy is language learning. If someone reads millions of books, they eventually internalize grammar, tone, and style well enough to write original sentences. Generative AI works similarly—except it does so at an unimaginable scale.
An easy way to start is to take a course from Udemy or Coursera, download models from Hugging Face, prepare a dataset, create batches, and train your model. Boom—you’ll have your own generative AI. It’s that simple; there’s no need to build everything manually.
Real-World Applications
Generative AI is no longer experimental; it’s already embedded in real workflows across industries.
Writers use AI tools to brainstorm ideas, overcome writer’s block, and draft content. Designers generate visual concepts in minutes instead of days. Developers rely on AI coding assistants to write, refactor, and debug code faster. Musicians experiment with AI-generated melodies and harmonies as creative inspiration.
In business, generative AI is used to draft marketing copy, summarize documents, generate reports, and create synthetic data for testing. In education, it supports personalized learning and tutoring. In healthcare, researchers are exploring its potential for drug discovery and medical imaging analysis.
Across all these fields, one theme is consistent: generative AI is becoming a creative partner rather than just a tool.
The Opportunities Ahead
The promise of generative AI lies in its ability to amplify human creativity and productivity. It reduces friction in the creative process, handles repetitive tasks, and provides instant access to knowledge and ideas.
People without formal design training can create professional-quality visuals. Individuals with limited programming experience can build functional applications. Teams can prototype ideas in hours instead of weeks.
By lowering barriers to entry, generative AI is democratizing creation. It enables rapid experimentation and allows more people to turn ideas into reality, faster and with fewer resources than ever before.
The Challenges We Can’t Ignore
Despite its potential, generative AI comes with serious considerations.
These systems can produce content that sounds confident but is factually incorrect. Questions around copyright, attribution, and the use of training data remain unresolved. There are also valid concerns about misuse, such as misinformation, impersonation, and deepfakes.
Additionally, generative AI raises questions about the future of work, particularly in creative and knowledge-based professions. While many experts believe it will augment rather than replace human roles, the transition will require adaptation, reskilling, and thoughtful policy decisions.
The real question isn’t whether generative AI will change society; it’s how responsibly we guide that change.

Explain more about it
I thing you should explain more