MongoDB is a powerful NoSQL database that pairs perfectly with Next.js for full-stack applications. In this guide, you’ll learn how to connect Next.js to MongoDB (locally or with MongoDB Atlas) using Mongoose, and how to build simple API routes to insert and retrieve data.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following installed:
- Node.js
- MongoDB (or MongoDB Atlas)
- A new or existing Next.js project
Create a Next.js app if needed:
npx create-next-app@latest next-mongo-app
cd next-mongo-appAlthough there is a small code change if you want to use TypeScript, I suggest using JavaScript for learning purposes.
Step 1: Install Mongoose
npm install mongooseSet the MongoDB URI in the .env.local file in your root directory
MONGODB_URI=mongodb://<username>:<password>@localhost:27017/<databaseName>?authSource=admin
//example
MONGODB_URI=mongodb://admin:12345@localhost:27017/nextjsdb?authSource=adminStep 2: Set Up MongoDB Connection Helper
Create a folder name lib and a file lib/mongodb.js:
Make sure you are connected to the MongoDB database
// lib/mongodb.js
import mongoose from 'mongoose';
const MONGODB_URI = process.env.MONGODB_URI;
if (!MONGODB_URI) {
throw new Error('Please define the MONGODB_URI environment variable');
}
let cached = global.mongoose;
if (!cached) {
cached = global.mongoose = { conn: null, promise: null };
}
export async function connectToDatabase() {
if (cached.conn) return cached.conn;
if (!cached.promise) {
cached.promise = mongoose.connect(MONGODB_URI, {
bufferCommands: false,
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true,
}).then((mongoose) => mongoose);
}
cached.conn = await cached.promise;
return cached.conn;
}
Step 3: Define a Mongoose Model
Create a folder models and a file models/Post.js
// models/Post.js
import mongoose from 'mongoose';
const PostSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
title: String,
content: String,
}, { timestamps: true });
export default mongoose.models.Post || mongoose.model('Post', PostSchema);Step 4: Create an API Route
Create pages/api/posts.js:
// pages/api/posts.js
import { connectToDatabase } from '../../../lib/mongodb';
import Post from '../../../models/Post';
export default async function handler(req, res) {
await connectToDatabase();
if (req.method === 'GET') {
const posts = await Post.find({});
return res.status(200).json(posts);
}
if (req.method === 'POST') {
const post = await Post.create(req.body);
return res.status(201).json(post);
}
return res.status(405).json({ message: 'Method not allowed' });
}Step 5: Test with a Frontend Form
Update pages/index.js With a simple form:
This will show in the home URL / in the browser a simple form for inserting data into the database
// pages/index.js or any component
'use client'; // if using App Router
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function Home() {
const [title, setTitle] = useState('');
const [content, setContent] = useState('');
async function handleSubmit(e) {
e.preventDefault();
const res = await fetch('/api/posts', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({ title, content })
});
const data = await res.json();
console.log(data);
// Clear form after submit
setTitle('');
setContent('');
}
return (
<div style={{ maxWidth: 500, margin: '0 auto' }}>
<h1>Create Post</h1>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<div>
<label>Title:</label>
<input
type="text"
value={title}
onChange={(e) => setTitle(e.target.value)}
required
style={{ width: '100%', padding: '8px', marginBottom: '10px' }}
/>
</div>
<div>
<label>Content:</label>
<textarea
value={content}
onChange={(e) => setContent(e.target.value)}
required
rows={5}
style={{ width: '100%', padding: '8px', marginBottom: '10px' }}
></textarea>
</div>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
);
}
Folder Structure Overview
Your folder structure should look the same. I have created:
myproject/
├── lib/
│ └── mongodb.js
├── models/
│ └── Post.js
├── pages/
│ ├── api/
│ │ └── posts.js
│ └── index.js
├── .env.local
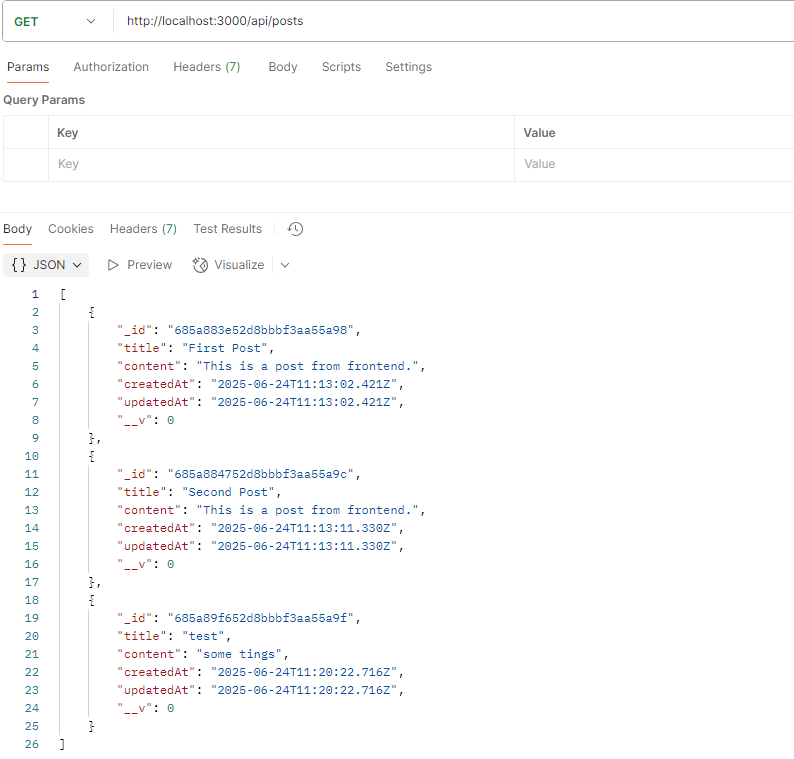
└── ...Api output should look like this :
Comment below, let me know how you start your next JS journey

