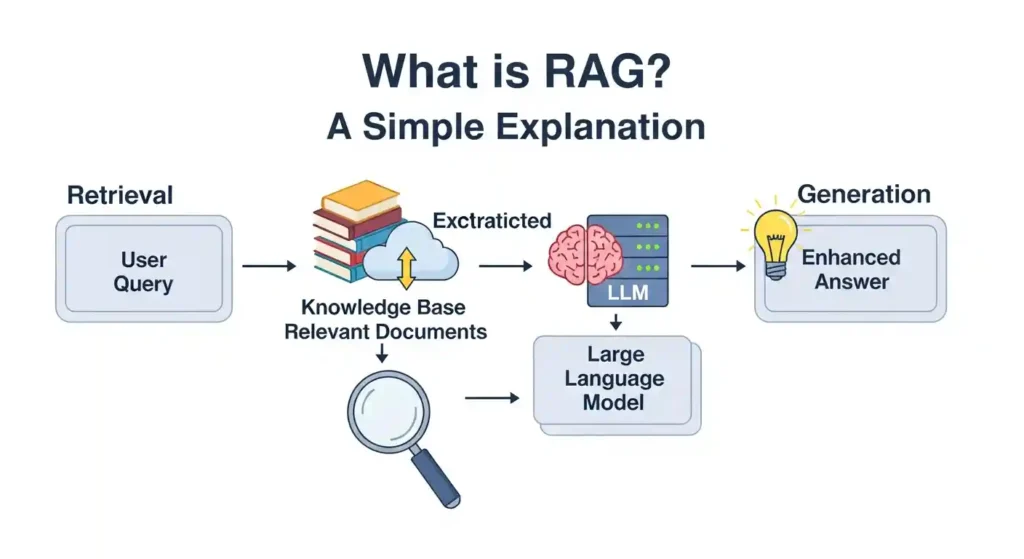
So you’ve undoubtedly heard the term “RAG” thrown around in AI chats and are wondering what it means. Don’t worry, it’s not as complicated as it seems, and I’ll explain it in plain English.
The Basics
RAG stands for Retrieval-Augmented Generation. I know that sounds super technical. But here’s the thing: it’s actually a pretty clever solution to a problem that AI models have been dealing with for a while now.
Think about it this way. You know how sometimes you’re chatting with an AI, and it just makes stuff up? Like, it sounds confident, but it’s completely wrong? That’s called hallucination, and it happens because these models are basically working from memory. They were trained on a bunch of data up until a certain point, and after that, they’re flying blind.
So What Does RAG Actually Do?
This is where RAG comes in. RAG allows the AI to look things up first, rather than depending just on what it learnt during training. It’s similar to the difference between answering a question from memory and quickly Googling it before responding.
The process works in three main steps:
First, there’s the retrieval part. When you ask a question, the system searches through a database or collection of documents to find relevant information. This could be your company’s internal docs, a knowledge base, recent articles, whatever you’ve set it up to access.
Then comes the augmentation. The AI takes that retrieved information and adds it to your original question. So now it’s not just working with what you asked, it’s also got fresh, relevant context to work with.
Finally, there’s the generation. The AI uses both your question and the retrieved information to generate a response. The result? Answers that are way more accurate and grounded in facts.
Why Should You Care?
RAG is a game-changer if you’re developing anything with AI that requires accuracy and up-to-dateness. Here’s why I believe it matters:
You obtain improved accuracy because the AI uses real sources rather than just winging it. You can maintain information up to date without having to retrain your entire model each time something changes. And honestly? It simply increases the overall credibility of the situation. When an AI can point to where it received its information, that’s huge.
I’ve seen this utilized for customer care chatbots that need to reference the most recent product documentation, research assistants that use scientific articles, and even internal company systems that help staff access information faster.
The Real-World Picture
Now, I am not going to sit here and say RAG is perfect. Setting it up requires some effort; you must arrange your papers, develop embeddings (which are essentially ways to make text searchable), and manage your database. Yes, it adds some latency because the system needs to search before responding.
But what about my experience? The trade-off is usually worthwhile. Especially if accuracy is important in your use case.
Wrapping Up
Finally, RAG’s primary goal is to improve AI’s reliability and utility. Instead of having a model that is stuck in the past and prone to making things up, you get one that can relate to current, correct data.
It’s not magic, but it comes close. And if you’re working on something that requires AI to offer correct, up-to-date responses, it’s certainly worth investigating.
Have you ever used RAG in any of your projects? I would love to hear about it. Leave a remark below and let’s talk about it.